Women’s Health: How Does Birth Control Cause Blood Clots?
Women who take birth control pills are at a higher risk of developing DVT and other forms of venous disease such as varicose veins. Hormone combinations in these pills increase clotting factors and cause platelet clumping that lead to clots. Women who are on birth control are told to stretch and walk around often to maintain healthy blood flow and prevent blood clots, especially women over 35 and women who frequently travel. Women with a family history of DVT, a personal history of DVT or multiple miscarriages should discuss this with their physician prior to starting birth control pills or hormone replace. If you have this history, you should be tested for a coagulopathy or an inherited or acquired tendency to develop DVT.
Women’s Health: How Common Are Blood Clots From Birth Control ?
Women using a newer form of birth control pills containing cyproterone, drospirenone, gestodene or desogestrel hormones are approximately four times more likely to develop a blood clot than women who do not use birth control. Alternatively, the risk is only about 2.5 times higher if you use an older form of the pill that contains norgestimate, levonorgestrel or norethisterone. This means that 14 out of every 10,000 women using newer birth control pills are expected to develop a blood clot, while six out of every 10,000 women using older pills may develop one.
Women’s Health: How Common Are Blood Clots In Pregnancy?
 Women are four times more likely to develop a blood clot during pregnancy. This risk is especially high during the third trimester. About one or two out of every 1,000 pregnant women will develop blood clots, and this risk increases as you age and with each new pregnancy.
Women are four times more likely to develop a blood clot during pregnancy. This risk is especially high during the third trimester. About one or two out of every 1,000 pregnant women will develop blood clots, and this risk increases as you age and with each new pregnancy.
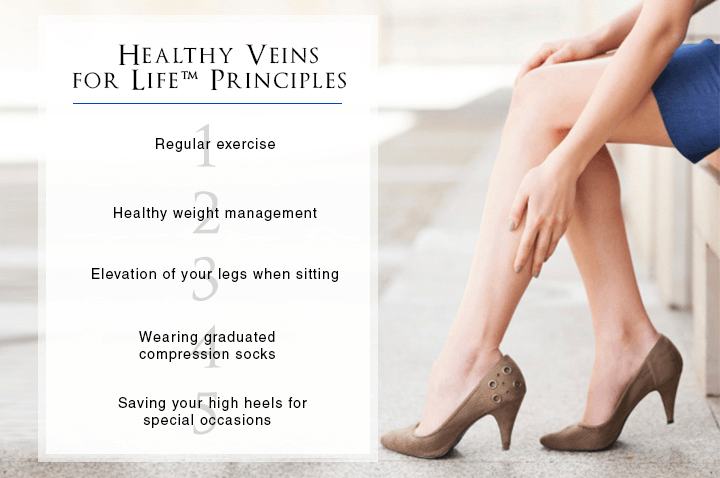
If you are pregnant, remember to elevate your legs, stretch often, and exercise to speed up the venous blood flow and prevent blood clots and varicose veins. If you already have varicose veins, wearing graduated medical grade compression hose during pregnancy can help with the symptoms, slow worsening of the varicose veins and lower your risk of developing a blood clot.
Women’s Health: Are Women At A Higher Risk Immediately After Childbirth?
Women are at a higher risk of developing blood clots during the first six weeks after delivery. Your risk during this time is five times higher than it is during your last trimester of pregnancy. Doctors advise light stretching and leg elevation after giving birth to decrease the risk of blood clots in the postpartum recovery period. If you develop symptoms of increased leg swelling, pain or shortness of breath, seek medical attention immediately.
Women’s Health: Blood Clots In Older Adults And The Elderly
Two major risk factors for developing DVT are inactivity and surgery, which are both common among the elderly. While fewer than 55,000 adults younger than 40 will be hospitalized for blood-clot-related issues, that number increases dramatically to more than 350,000 when the adult is older than 60. Older women make up the majority of that group.
Women’s Health: Risk Assessment, Prevention And Treatment
Traveling, inactivity, surgery, pregnancy and hormonal contraceptives increase your risk of developing DVT. You can lower these risks by wearing compression stockings and adhering to a healthy, active lifestyle. If you are frequently inactive for any reason, take medications that affect blood coagulation or are pregnant, contact us at Vein Specialists of the South to create the best DVT-prevention strategy. We want to help you live a long, healthy life free of the effects of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism.


 Women are four times more likely to
Women are four times more likely to